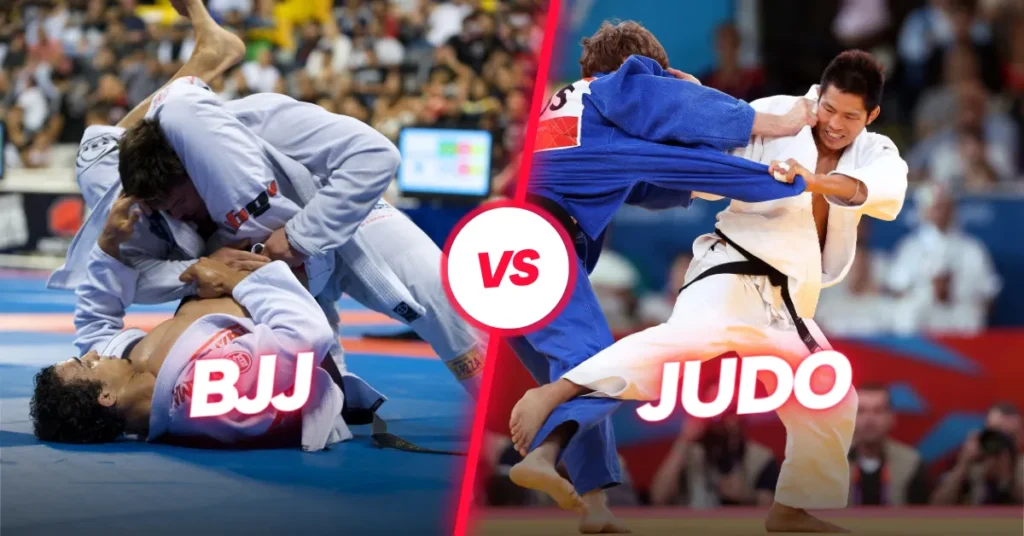
Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu (BJJ) and Judo are two of the most well-known grappling-based martial arts styles. Although they both have roots in traditional Japanese Jiu-Jitsu, they have developed into unique forms with disparate specializations. Judo lays more emphasis on throws and takedowns than BJJ does on ground fights and submissions.
Which one should you choose if you want to excel in self-defense situations or submission wrestling? Join us in this article as we delve deep into the intriguing comparison of BJJ vs Judo.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- BJJ and Judo are grappling-based martial arts with different areas of focus.
- BJJ places an emphasis on ground fighting and submissions, while Judo focuses on throws and takedowns.
- The choice between BJJ and Judo depends on individual preferences and goals.
- Training in both styles can complement each other and enhance overall grappling skills.
- Both BJJ and Judo can be effective for self-defense, depending on the individual’s skill level and ability to adapt.
History of Judo
Judo has a rich history rooted in traditional Japanese Jiu-Jitsu. It was developed as a fighting system for the Samurai, the dominant caste of warriors during Japan’s feudal era.
Judo incorporates throws, armlocks, chokes, and techniques specifically designed for combating opponents wearing armor. The founder of Judo, Jigoro Kano, opened the first Kodokan Judo school in 1882, modifying traditional Jiu-Jitsu to make it more accessible and acceptable to the masses. Judo gained popularity and eventually became an Olympic sport in 1964.
Judo’s Samurai Origins
Judo’s roots can be traced back to the samurai, the warrior class of feudal Japan. The samurai practiced various martial arts, including jujitsu, which laid the foundation for Judo. Jujitsu techniques were developed to allow the samurai to defeat their opponents in close combat, both armed and unarmed.
The Birth of Kodokan Judo
In the late 19th century, Jigoro Kano developed Judo based on his extensive study of different jujitsu styles. Kano aimed to create a system that emphasized practical techniques while also instilling discipline, respect, and character development in its practitioners.
“Judo is the way to the most effective use of both physical and spiritual strength.”
Kano named his new martial art “Judo,” which translates to “gentle art.” He established the Kodokan, a training school, in Tokyo, where he refined and popularized Judo as a distinct martial art.
Judo’s Evolution and Global Spread
Kano’s efforts to promote Judo were not limited to Japan. He traveled extensively, spreading the art worldwide and fostering international relationships. Judo gradually gained popularity in other countries and became an Olympic sport with its inclusion in the 1964 Tokyo Olympics.
The Philosophy of Judo
Kano envisioned Judo not only as a means of self-defense but also as a path for personal growth and moral development. He emphasized the importance of mutual respect, self-discipline, and using one’s skills for the benefit of both oneself and society.
| Judo | Jujitsu |
|---|---|
| Emphasizes throws, armlocks, and chokes | Focuses on a broader array of techniques, including strikes and weapons training |
| Developed for use against opponents wearing armor | Primarily employed by the samurai in various combat scenarios |
| Founded by Jigoro Kano in 1882 | Origins trace back to ancient Japanese martial arts |
| Includes moral and character development | Less emphasis on moral teachings |
The Origins of Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu
Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu (BJJ) has a fascinating history that traces its roots back to Kodokan Judo. In 1914, a judoka named Mitsuyo Maeda, also known as Count Koma, traveled to Brazil and introduced Judo to the country. Maeda’s teachings greatly influenced the Gracie family, particularly Carlos and Helio Gracie, who recognized the potential of the ground aspect of Judo, known as “newaza.”
Carlos and Helio Gracie studied Judo and started to focus heavily on ground fighting techniques. They refined and expanded their knowledge, eventually creating Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu as a distinct martial art. The Gracies understood the effectiveness of ground fighting, as it allowed a smaller and weaker opponent to overcome a larger and stronger adversary through leverage, technique, and submissions.
The Gracie family’s ground fighting system was put to the test in the legendary Vale Tudo fights, a no-holds-barred style of combat prevalent in Brazil. The Gracies dominated these matches, showcasing the effectiveness of Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu in real combat situations.
This success paved the way for the establishment of the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) in 1993, the first mixed martial arts promotion. Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu became a cornerstone of the UFC, as fighters with BJJ skills consistently demonstrated their ability to control opponents on the ground and secure submissions.
Differences in Technique and Focus
The primary difference between BJJ and Judo lies in their techniques and areas of focus. Judo places a greater emphasis on throwing techniques, including trips, foot sweeps, and throws executed from standing and clinch positions. The goal in Judo is to quickly and effectively throw an opponent to the ground in order to secure victory.
BJJ, on the other hand, focuses on ground fighting, where practitioners aim to control and submit opponents using various techniques. The emphasis is on grappling on the ground, with an emphasis on submissions such as chokes and armlocks. BJJ practitioners learn how to maneuver and dominate their opponents in close quarters on the mat.
While both styles incorporate joint locks and throws, they prioritize different aspects of grappling. Judo practitioners focus on explosive throws and takedowns to gain a dominant position, while BJJ practitioners work on controlling and submitting opponents on the ground.
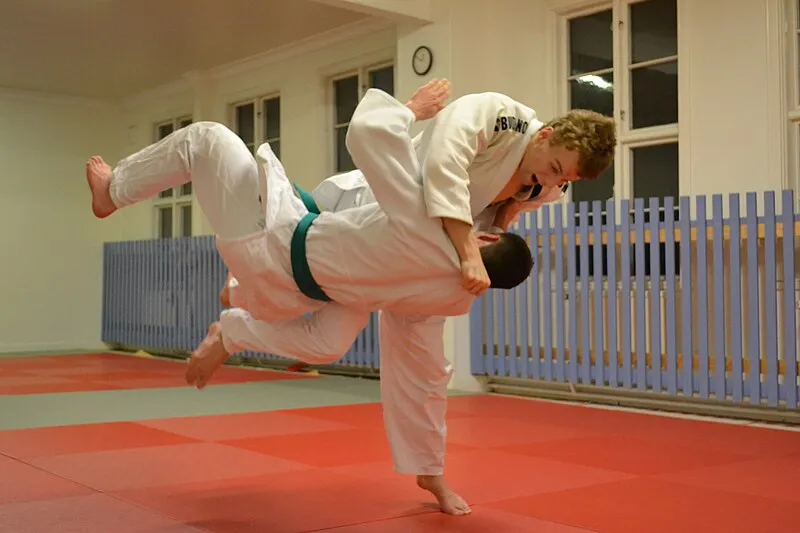
Throwing Techniques in Judo
Judo is known for its wide array of throwing techniques, many of which utilize an opponent’s momentum against them. Common throwing techniques in Judo include:
- Osoto Gari – Major Outer Reap
- Seoi Nage – Shoulder Throw
- Ogoshi – Hip Throw
- Uchi Mata – Inner Thigh Throw
- Harai Goshi – Sweeping Hip Throw

Ground Fighting and Submissions in BJJ
BJJ practitioners excel in ground fighting, utilizing leverage, technique, and strategy to dominate their opponents. Key techniques employed in BJJ ground fighting include:
- Guard Passes – Techniques for breaking an opponent’s guard
- Sweeps – Techniques for reversing an opponent’s position
- Mount Control – Establishing a dominant position on top
- Submissions – Techniques such as chokes and armlocks to force an opponent to submit
- Escapes – Techniques for freeing oneself from disadvantageous positions
BJJ practitioners become adept at transitioning between positions on the ground and applying submissions to secure victory.
“Judo places a strong emphasis on throwing techniques, allowing practitioners to quickly gain the advantage in a fight. BJJ, on the other hand, focuses on ground fighting and submissions, providing the skills needed to control and defeat opponents on the mat.”
Rule Differences Between Judo and BJJ
Judo and Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu (BJJ) follow distinct rule sets that influence the way matches are won and the techniques that are emphasized. Understanding these differences is key to appreciating the unique aspects of each martial art.
Judo Rules
Judo matches have specific criteria for victory. The highest-scoring outcome is an “ippon,” which can be achieved in several ways. An ippon can be earned by executing a powerful throw that forces the opponent onto their back with speed, control, and impact. Another ippon-worthy move is successfully submitting the opponent through joint locks or chokes. Additionally, pinning an opponent for 20 seconds, known as “osae-komi,” also results in an ippon. Accumulating two “waza-aris,” which are lower-scoring throws, can also lead to victory. The accumulation of penalties, known as “shidos,” can also determine the winner when there is no ippon or waza-ari scored.
BJJ Rules
BJJ matches are predominantly ground-focused and aim to simulate real-life self-defense scenarios. Points are awarded for various actions during the match. Points are allocated for executing successful takedowns, sweeps (reversing positions from the bottom), passing the guard (moving past an opponent’s legs), and attaining dominant positions such as mount or back control. Submissions, where an opponent taps out due to a joint lock or chokehold, immediately end the match in victory. Points accumulated during the match serve as tiebreakers if no submissions occur.
The differing rule sets reflect the historical evolution and specific goals of each style. Judo prizes takedowns and throws as a means of rapid and forceful victory, while BJJ prioritizes control, positioning, and submission techniques on the ground to achieve dominance and submission.
| Judo | BJJ |
|---|---|
| Ippon – Forceful throw or submission | Points – Takedowns, sweeps, passing guard, dominant positions |
| Waza-ari – Lower-scoring throws | Submissions – Joint locks, chokes |
| 20 seconds pin | Points as tiebreakers |
| Penalties (Shidos) | – |
Belt Systems and Grading
Both Judo and BJJ have belt systems that serve as a visual representation of a practitioner’s progress and skill level. The belt progression in Judo typically consists of six belts before reaching the prestigious black belt. The progression begins with the white belt and continues with the yellow, orange, green, blue, and brown belts. BJJ, on the other hand, follows a similar path but with five belt colors leading up to the black belt. The journey starts with the white belt and progresses to the blue, purple, brown, and finally, the revered black belt.
Earning a higher belt rank in both Judo and BJJ requires consistent training, dedication, and the acquisition of technical knowledge. Practitioners engage in regular practice sessions, refining their skills, and learning new techniques as they progress through the belt system. Instructors evaluate the practitioners’ performance, ensuring they meet the requirements for advancement to the next belt color.
The black belt holds significant significance in both Judo and BJJ, representing a high level of proficiency and mastery in the art. Achieving the black belt in either discipline requires years of dedication and a deep understanding of the principles and techniques involved. It symbolizes the culmination of years of training and serves as a testament to the practitioner’s dedication, discipline, and expertise.
| Judo Belt Ranking | BJJ Belt Ranking |
|---|---|
| White | White |
| Yellow | Blue |
| Orange | Purple |
| Green | Brown |
| Blue | Black |
| Brown | |
| Black |
Learn more about Judo belts and BJJ belts: Judo Belt Guide & BJJ Belts Ranking System Explained
Equipment and Uniforms
In the world of martial arts, both Judo and Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu (BJJ) require practitioners to wear specialized uniforms known as gis. While there are some similarities between the two, there are also distinct differences in the design and requirements of these uniforms.
Judo Gis
Judo gis are specifically designed to withstand the intense grappling and throwing techniques inherent to the art. They are typically heavier and more durable than BJJ gis. Made from a thick and robust material, Judo gis are designed to withstand the rigors of regular training and competition. The pants of a Judo gi are usually wider and looser to allow for increased mobility and flexibility during throwing techniques.
In Judo competitions, the use of either a white or blue gi is required. The color of the gi can serve as an identifier for scoring purposes, ensuring clear visibility and differentiation between competitors. The belt worn with the gi reflects the practitioner’s skill level, with a series of different colored belts signifying progression and rank within the system.

BJJ Gis and No-Gi Option
BJJ gis, while also durable, are often made from a lighter and more flexible material. This design choice allows for improved maneuverability, especially during ground fighting and submission techniques. BJJ gis typically have a slimmer fit and more streamlined appearance compared to Judo gis.
In BJJ competitions, various colors of gis are allowed, providing individuals with the opportunity to express their personal style. From white and blue to black and even vibrant colors, the choice of gi color in BJJ competitions is more open-ended, allowing practitioners to showcase their unique personalities on the mats.
Furthermore, BJJ also offers a no-gi option, where practitioners can participate in training and competition without wearing a gi. Instead, rash guards or compression shirts, along with shorts or spats, are worn to provide grip and minimize skin-to-skin contact while facilitating movement during ground exchanges.

Summary Comparison
| Criteria | Judo Gis | BJJ Gis |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Thicker and more durable | Lighter and more flexible |
| Pants | Wider and looser | Slimmer and more fitted |
| Color Options | White or blue | Various colors |
| No-Gi Option | N/A | Rash guards and shorts |
While both Judo gis and BJJ gis serve their respective purposes, the choice between them ultimately depends on a practitioner’s martial arts goals and personal preferences. Whether it’s the rigorous throws of Judo or the ground-based techniques of BJJ, having the appropriate gi is important for performance and adherence to competition regulations.
Competitive Landscape
Both Judo and Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu (BJJ) have vibrant competitive scenes that offer athletes opportunities to showcase their skills and compete at various levels. Let’s explore the competitive landscape for each martial art.
Judo Competition
Judo has a rich tradition of organized tournaments at the local, regional, national, and international levels. These competitions provide a platform for judoka (Judo practitioners) to test their skills, gain experience, and strive for excellence. One of the most significant highlights for Judo is its inclusion as an Olympic sport. Being an Olympic event grants Judo global recognition and captivates a massive audience during the Games.
“Judo’s recognition as an Olympic sport has elevated its status and attracted talented athletes worldwide.” – International Judo Federation
Judo tournaments adhere to strict rules and regulations that emphasize throwing techniques, ground control, and effective grappling. Athletes compete in weight categories, ensuring fair matches based on physical attributes. The competitive spirit and technical prowess displayed in Judo competitions make it a thrilling martial art to watch and participate in.
| Tournament | Description |
|---|---|
| Olympic Games | The pinnacle of Judo competition, where the best judoka from around the world compete for gold, silver, and bronze medals. |
| World Championships | A biennial event that brings together top judoka to compete for the title of world champion in various weight categories. |
| Continental Championships | Regional competitions where judoka from specific continents compete against each other, showcasing their skills and aiming for qualification to higher-level tournaments. |
| National Championships | Country-level competitions held annually, where judo practitioners compete for national titles and a chance to represent their country internationally. |
| Local and Regional Tournaments | Smaller-scale competitions that provide opportunities for judoka of all levels to gain experience, test their skills, and interact with the Judo community. |
These Judo competitions contribute to the growth and development of the sport, providing a platform for talented athletes to showcase their skills and inspire the next generation of judoka.
BJJ Tournaments
BJJ tournaments have gained significant popularity worldwide and are organized by various governing bodies, with the International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation (IBJJF) being one of the most prominent. These tournaments offer BJJ practitioners a platform to compete, win titles, and progress through the belt ranks.
“BJJ tournaments provide a competitive outlet for practitioners to challenge themselves, test their skills, and measure their progress.” – International Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Federation
BJJ competitions, like Judo tournaments, adhere to specific rulesets designed to ensure fair matches and encourage skillful grappling. BJJ tournaments feature a range of divisions based on age, weight, and belt rank, allowing practitioners to compete against opponents of similar skill levels.
| Tournament | Description |
|---|---|
| IBJJF World Championships | Considered the most prestigious BJJ tournament, attracting elite grapplers from around the world and crowning world champions in various weight categories and belt ranks. |
| IBJJF Pan-American Championships | A popular BJJ tournament held annually in the United States, bringing together top North and South American competitors to battle for the title of champion. |
| National and Regional Tournaments | Country-level and regional competitions that provide opportunities for BJJ practitioners to compete, gain experience, and earn recognition within their respective communities. |
| Open Tournaments and Invitational Events | Smaller-scale tournaments and invitation-only events organized by local academies or independent promoters, showcasing talent from different BJJ affiliations. |
BJJ tournaments offer a platform for practitioners to test their skills and gauge their progress. They foster a competitive spirit while promoting sportsmanship and camaraderie within the BJJ community.
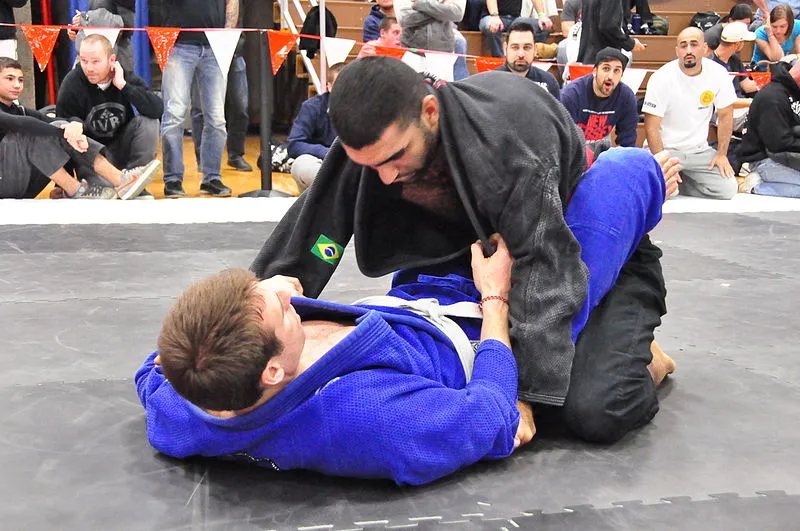

Effectiveness for Self-Defense
Both BJJ and Judo can be highly effective martial arts for self-defense due to their emphasis on grappling techniques. When it comes to real-life self-defense situations, where fights often end up on the ground, BJJ’s focus on ground fighting and submissions can provide a significant advantage. By utilizing techniques such as sweeps, transitions, and submission holds, practitioners can neutralize their opponents and gain control of the situation.
On the other hand, Judo’s emphasis on throws and takedowns can also be highly effective in self-defense scenarios. A Judoka’s ability to execute powerful throws can quickly incapacitate an attacker and create an opportunity to escape or gain dominance in the encounter.
However, the effectiveness of either style for self-defense ultimately relies on the individual’s skill level, training, and ability to adapt to different situations. Both BJJ and Judo require dedicated practice, discipline, and a thorough understanding of their respective techniques to maximize their effectiveness in real-world self-defense scenarios.
It is worth noting that self-defense situations can vary greatly and may involve multiple opponents, weapons, or unpredictable circumstances. In such cases, it is essential to have a well-rounded approach to self-defense that may include other martial arts disciplines, awareness training, and practical self-defense techniques beyond grappling.
Fitness
| Feature | BJJ | Judo |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Groundwork, control through technique and flexibility | Throws and takedowns, immobilizing opponents |
| Strength Focus | Core strength, agility, joint mobility | Explosive power, upper body strength for throws, lower body strength for balance |
| Cardio | High-intensity bursts during scrambles and transitions | Intense interval training with explosive movements and short rest periods |
| Body Composition | Leaner muscle development, emphasizes control | More muscular development, focus on power and explosiveness |
BJJ
By emphasizing foundation, BJJ places a high priority on honing core strength, agility, and joint mobility. Transitional high-intensity bursts enhance cardiovascular endurance, while the focus on regulated procedures precisely develops lean muscle.
Judo
The core of judo fitness is explosive power, which calls for strong lower body strength for stability and balance as well as strong upper body strength for throws. Judo’s cardio regimen consists of intense interval training with powerful motions that build muscle and emphasize strength and explosiveness.
BJJ is a good option for people looking for precision, agility, and the development of lean muscles. On the other hand, Judo might be a good option for people who want to gain more muscle mass, explosive power, and upper body strength. These two fields provide different paths to reach certain fitness goals, guaranteeing a rewarding path to improved physical health.
Complementing Skills and Training
Judo and BJJ are sister arts, sharing a common origin in traditional Japanese Jiu-Jitsu. Training in both styles can complement each other, enhancing overall grappling skills. Judo practitioners can benefit from learning BJJ’s ground fighting techniques, while BJJ practitioners can improve their takedowns and throws through Judo training. The crossover between the two styles allows practitioners to develop a well-rounded skill set that translates well across both sports.
By cross-training in Judo and BJJ, practitioners can expand their repertoire of techniques and gain a deeper understanding of the principles underlying grappling arts. Judo’s emphasis on throws and takedowns can enhance BJJ practitioners’ ability to control the standing position and execute effective takedowns. Judo’s focus on off-balancing and timing can improve BJJ practitioners’ ability to anticipate and counter their opponents’ movements. On the other hand, BJJ’s emphasis on ground fighting and submissions can provide Judo practitioners with a more comprehensive understanding of controlling and submitting opponents on the ground.
The complementarity between Judo and BJJ extends beyond techniques. Both arts prioritize physical fitness, mental discipline, and perseverance. The intense training involved in both Judo and BJJ builds endurance, strength, and flexibility, all of which are essential for successful grappling. Moreover, the mental aspects of training, such as focus, strategy, and problem-solving, are equally important in both arts.
By incorporating Judo and BJJ into their training regimen, practitioners can accelerate their progress and improve their overall grappling skills. The combination of Judo’s throws and takedowns with BJJ’s ground fighting and submissions creates a well-rounded skill set that is adaptable to a wide range of situations. Whether in the dojo, in competition, or in real-life self-defense scenarios, the complementary nature of Judo and BJJ provides practitioners with a valuable and comprehensive foundation in grappling arts.
Conclusion
After comparing the key differences between Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu (BJJ) and Judo, it is clear that both martial arts have their unique strengths and weaknesses. BJJ’s focus on ground fighting and submissions has proven to be highly effective in mixed martial arts (MMA) competitions, allowing practitioners to control and submit opponents on the ground. On the other hand, Judo’s emphasis on throws and takedowns provides valuable skills for self-defense situations and can quickly neutralize opponents.
When it comes to choosing between BJJ and Judo, personal preference and individual goals play a significant role. Some individuals may prefer the technical aspect of BJJ and the strategic nature of ground fighting, while others may find the explosive throws and takedowns of Judo more appealing. It is important to consider your own objectives, whether you are interested in self-defense, sport competition, or overall personal development.
Ultimately, many practitioners find value in training both BJJ and Judo, as the techniques learned in one style can greatly enhance the other. Cross-training allows for a well-rounded skill set that covers all aspects of grappling. By combining the ground fighting expertise of BJJ with the throwing proficiency of Judo, practitioners can become versatile martial artists, well-equipped for various scenarios.
In conclusion, the choice between BJJ and Judo should be based on individual preferences and goals. While some may prefer the ground dominance of BJJ, others may favor Judo’s explosive throws. Both martial arts have proven track records and dedicated communities. It is up to each individual to determine which style resonates with them the most, and to pursue their martial arts journey accordingly.
FAQ
What are the key differences between Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu (BJJ) and Judo?
BJJ focuses more on ground fighting and submissions, while Judo emphasizes throws and takedowns.
Is it better to learn Judo or BJJ?
The choice depends on personal preferences; Judo emphasizes throws, while BJJ focuses on submissions and groundwork. Choose based on individual interests and goals.
Can Judo defeat BJJ?
It depends on the context. Judo excels in throws, while BJJ is strong on the ground. The outcome relies on the skills and strategies of the practitioners.
Is Judo or BJJ better for a street fight?
Both have strengths; Judo’s throws can quickly control opponents, while BJJ’s groundwork and submissions are effective. Both can be applied in self-defense situations.
Is Judo or BJJ harder on the body?
Impact varies; Judo’s throws may stress joints, while BJJ’s close-contact grappling can lead to strain. Impact depends on individual factors, training intensity, and technique.
What techniques are emphasized in BJJ and Judo?
BJJ emphasizes ground fighting, submissions (chokes and armlocks), while Judo focuses on throws, takedowns, and techniques to neutralize armored opponents.
Can training in Judo and BJJ complement each other?
Yes, training in both styles can enhance overall grappling skills. Judo can improve takedowns and throws in BJJ practitioners, while BJJ can enhance ground fighting techniques for Judoka.